Home

Low Lying Placenta

What is Low-Lying Placenta: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Risk Factors and Travel Restrictions
In this Article
Low Lying Placenta
What is Low-Lying Placenta: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Risk Factors and Travel Restrictions
Updated on 3 November 2023



Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Shruti Tanwar
C-section & gynae problems - MBBS| MS (OBS & Gynae)
View Profile

A low-lying placenta and placenta previa are complications that can occur during pregnancy. This condition occurs when the placenta is implanted in the lower part of the uterus, covering or partially covering the cervix. While it is not a common complication, it can cause serious risks to both the mother and the baby.
In this article, we will discuss what low lying placenta means, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, risk factors, and travel restrictions associated with it. It is important for expectant mothers to be aware of this condition and to take necessary precautions to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
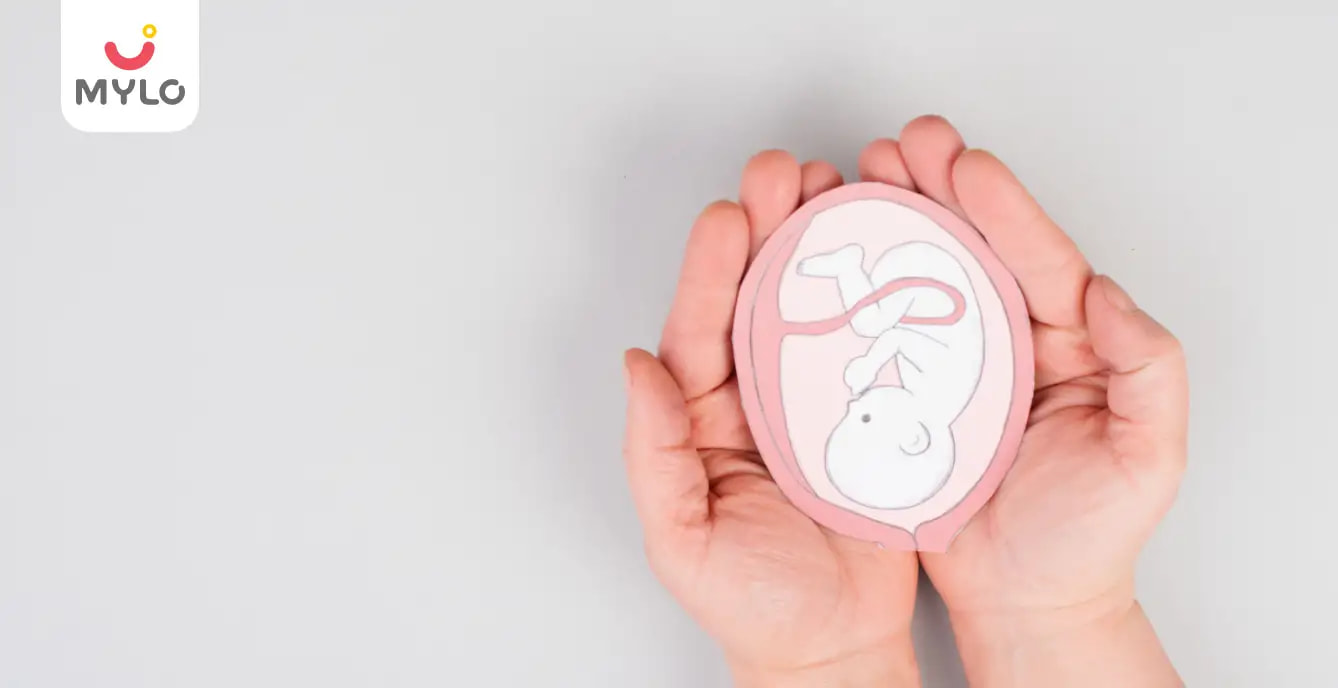
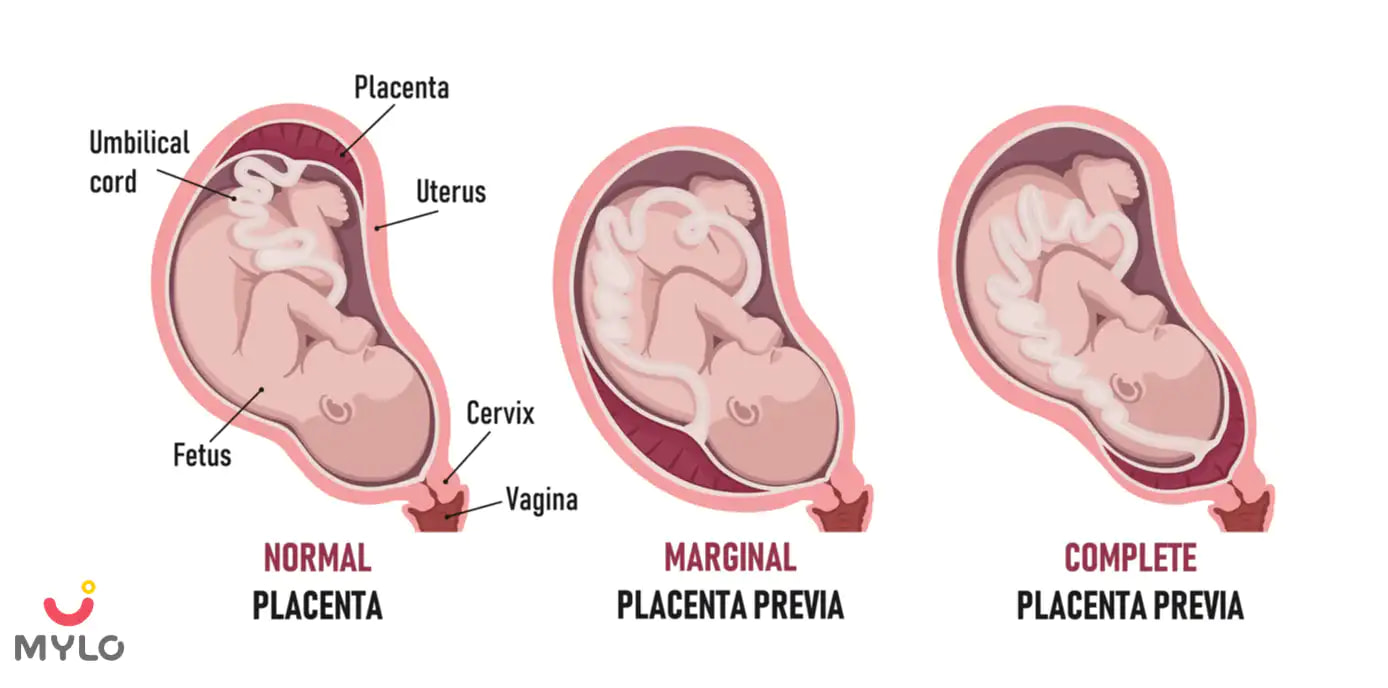
What is a low-lying placenta?
The placenta is a vital yet temporary organ that a woman’s body develops at conception to nourish the baby with essential nutrients, blood and oxygen. It also removes the waste from the body of the foetus. The development of a placenta can be detected in the early weeks of pregnancy, usually through an ultrasound. The placenta attaches itself to the lining of your womb. The placenta does not move from its attachment, but it can vary in size (Placental Migration) according to the growth of the uterus as the pregnancy progresses.
When the placental structure is attached to the lower part of the uterus near the cervix (the lower part of the uterus through which the baby is pushed out), a low-lying placenta is found in the ultrasound. A transvaginal scan is typical to find a low-lying placenta at 12 weeks of pregnancy. However, the placenta could move up later, causing little to no complications in labor and pregnancy. But in a few rare cases, the placenta could stay covering the cervix, partially or entirely blocking the birth route of the foetus. This condition is called placenta previa.
What are the causes of a low lying placenta?
The exact cause of low lying placenta remains unknown but there are certain factors that can increase your risk of of low lying placenta during pregnancy:
1. Previous cesarean delivery
Women who have had a previous cesarean section are at a higher risk of developing low-lying placenta in their subsequent pregnancies.
2. Multiple pregnancies
The placenta could be low when a mother is pregnant for the second time or with a twin or multiple foetuses.
3. Advanced maternal age
Women over the age of 35 have a higher risk of developing low-lying placenta.
4. Smoking
Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of placental problems, including placenta previa.
5. Uterine scarring
Women who have had surgery or an infection in their uterus may have scarring that can affect the position of the placenta.
6. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Women who conceive through IVF have a higher risk of developing low-lying placenta.
There are many reasons why this condition occurs during pregnancy, but it is essential to remember that a low-lying placenta is manageable. In addition, you can always reach out to your doctor to get clarity about the symptoms and treatment if your placenta is low-lying.
What are the symptoms of a low-lying placenta?
A low-lying placenta, also known as placenta previa, may not cause any symptoms in some women and may be detected during a routine ultrasound. However, some women may experience symptoms such as:
- Painless bright red vaginal bleeding after the 20th week of pregnancy
- A baby inside the womb generally engages in the third trimester (from 30 to 34 weeks), but mothers with a low-lying placenta may find their babies still in breech or other unfavourable positions even in the last few weeks.
- Cramps that mimic menstrual discomfort may occur frequently. This is also accompanied by bleeding.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms as they could indicate a more serious pregnancy complication.
Can low-lying placenta cause any complications?
Some of the most common complications associated with a low-lying placenta include:
- experiencing vaginal bleeding
- going into preterm labor
- placenta accreta (a condition where the placenta grows too deeply into the uterine wall)
- massive hemorrhage
- increased risk of a cesarean delivery
It is important for women with a low-lying placenta to receive regular prenatal care and follow their doctor's recommendations closely to minimize the risk of complications.
What precautions and travel restrictions to take for a low-lying placenta?
Although doctors and medical intervention cannot prevent the occurrence of placenta previa, they will always guide you with instructions and constant monitoring of the foetal and maternal well-being:
- Doctors will also make prior arrangements, foreseeing cases of blood transfusions during labour.
- Eating healthy and following a healthy lifestyle can help prevent anaemia during pregnancy.
- Your physician may suggest you abstain from intercourse if you find yourself bleeding after.
- Refraining from strenuous exercise routines and regular check-ups can help you stay positive.
- It is wise to restrict travel with a low-lying placenta. Consider avoiding air travel.
- Try to refrain from long-distance travel through other modes after 32-weeks.
- Your care provider will instruct you on how much bed rest you need to cope with the impacts of placenta previa.
- Medical health professionals advise that the right sleeping position for the low-lying placenta is by the left side so that there is the absence of pressure on the veins, ensuring better blood supply.
- As far as the sitting position for low-lying placenta is concerned, there are no restrictions but avoiding sitting for a long time.
What are the treatments needed for a low-lying placenta?
You will be requested to visit the hospital for frequent scans. For example, if your ultrasound shows signs of a low-lying placenta at 20 weeks, another scan will be scheduled at 32 weeks to find the position of the placenta. If the symptoms and blockage of the cervix continue to be visible even at 36 weeks, your doctor will plan your delivery with your consent at an early stage. This shall ensure the safety of the mother and the foetus.
If the labour happens prematurely, you will be given steroid injections to aid the maturity of the foetal lungs. Sometimes, things may not go as planned, especially with severe bleeding before delivery. As a result, the doctor may opt for an emergency C-section to avoid further complications.
A low-lying placenta needs consistent monitoring, so please do not skip your prenatal visits or scheduled scans. Instead, ask your doctor questions to be updated on the health status of you and the little one. With early diagnosis and the right medical decisions, you and your baby can have a positive birthing experience.
Summary
Low-lying placenta is a condition where the placenta is attached to the lower side of the uterus, potentially covering the cervix. In most cases, the position of the placenta may turn out to be favourable after 30 weeks of gestation. If the low-lying placenta persists in the third trimester, it may cause bleeding, difficulty in labour and premature delivery. In such cases, doctors may suggest early or caesarean delivery. It is essential to follow a healthy lifestyle, have regular check-ups, and keep in mind the travel restrictions and precautions.
References
- Heller HT, Mullen KM, Gordon RW, Reiss RE, Benson CB. (2014). Outcomes of pregnancies with a low-lying placenta diagnosed on second-trimester sonography. J Ultrasound Med. NCBI
- Anderson-Bagga FM, Sze A. Placenta Previa. (2022). Placenta Previa. NCBI
- Faiz AS, Ananth CV. (2003). Etiology and risk factors for placenta previa: an overview and meta-analysis of observational studies.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med
Trending Articles
public breastfeeding | Sex After Delivery | thyroid cancer symptoms in female | breastfeeding and formula feeding schedule
Popular Articles
postpartum constipation | how to massage newborn baby | baby walking | signs baby will walk soon





Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Shruti Tanwar
C-section & gynae problems - MBBS| MS (OBS & Gynae)
View Profile


Written by
Priyanka Verma
Priyanka is an experienced editor & content writer with great attention to detail. Mother to an 11-year-old, she's a ski
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |