Home

Diabetes during Pregnancy

Blood Sugar Levels in Pregnancy: What You Should Know
In this Article

Diabetes during Pregnancy
Blood Sugar Levels in Pregnancy: What You Should Know
Updated on 3 November 2023
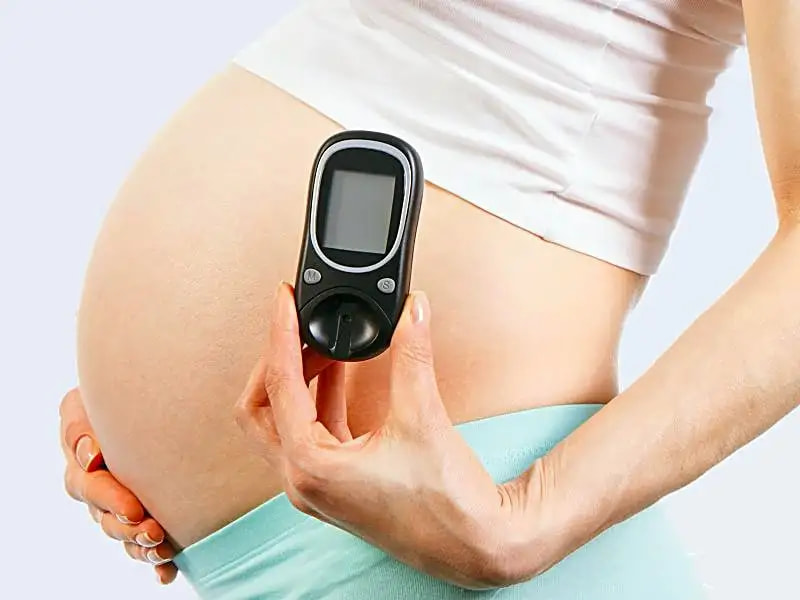
Increased blood sugar levels in pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), has become a prevalent phenomenon in India. It is a major public health concern as about 4 million women are affected by GDM in India at any given time. GDM is seen in pregnant women because of insulin resistance due to hormonal activity. This hormone is made by the placenta that stops blood from utilising insulin as it would otherwise. This causes blood sugar to pile up rather than get absorbed by your body's cells. Usually begins about 20 to 24 weeks.
Causes of high blood sugar levels in pregnancy
Here are some of the causes of high blood sugar levels in pregnancy:
-
Overweight or obese
-
Physically inactive
-
Prediabetes
-
History of gestational diabetes during previous pregnancies
-
Family history of diabetes
What is the normal blood sugar level for a pregnant woman?
According to the American Diabetic Association, the following target should be maintained for normal blood sugar levels for a pregnant woman without diabetes:
Before a meal: 90 mg/dl or less. One hour post a meal: 130–140 mg/dl or less. Two hours post a meal: 120 mg/dl or less.
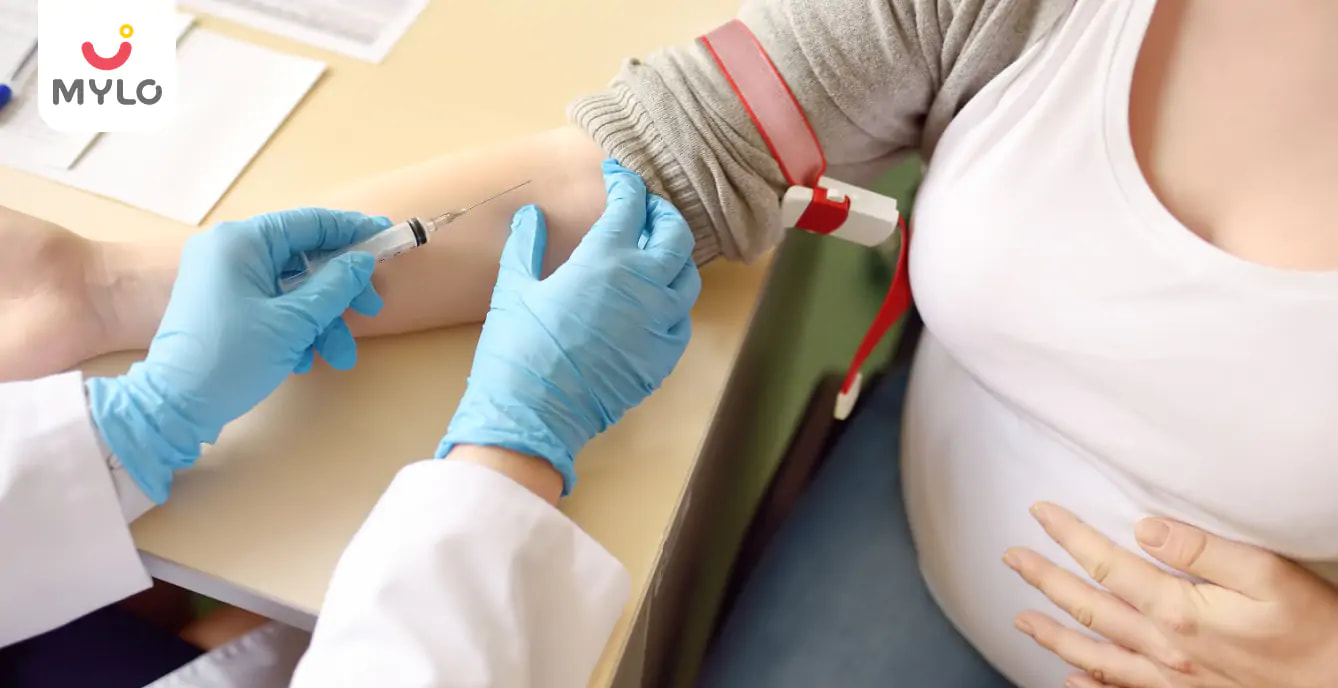
To maintain optimal blood sugar levels, the expecting mother should record the readings of blood sugar by a simple home test. This involves a simple finger prick before and after meals. Continuous glucose monitoring or a 2-hour test may be suggested based on one's requirements.
What is the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman with diabetes?
The blood sugar level in the screening test is high if it is above 130 to 140 mg/dL. For example, a 160 Sugar Level During Pregnancy; will be considered high. If the blood sugar levels are very high (≥200 mg/dL), there is a very strong chance that gestational diabetes is present.
Effects of high blood sugar during pregnancy
The following can be the effects of high blood sugar levels in pregnancy:
1. Risk of Injury
There is an increased risk of injury to the mother or baby during labour, and the possibility of birth by cesarean is increased.
2. Macrosomia
Large babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes are at a bigger risk of developing diabetes and obesity during their lifetime.
3. Neonatal hypoglycemia
There is an increases risk of low blood sugar in the newborn. They may also have low levels of magnesium and calcium in their blood.
How to lower blood sugar during pregnancy?
Managing blood sugar during pregnancy is crucial, especially if you have gestational diabetes or are at risk for developing it. Here are some general tips that may help lower blood sugar levels during pregnancy:
1. Healthy diet
Focus on a balanced and nutritious diet that includes a variety of whole foods. Aim to consume plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary and processed foods.
2. Monitor carbohydrate intake
Carbohydrates can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Try to choose complex carbohydrates with a lower glycemic index, as they cause a slower rise in blood sugar. Examples include whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
3. Regular meals and snacks
Eating regular meals and snacks throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar.
4. Portion control
Be mindful of portion sizes to prevent large spikes in blood sugar levels.
5. Physical activity
Regular exercise, as approved by your healthcare provider, can help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Engage in activities like walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga, depending on your fitness level and medical condition.
6. Stay hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help with blood sugar management.
9. Medication and insulin
If you have gestational diabetes or diabetes that existed before pregnancy, your healthcare provider may recommend medication or insulin to help manage blood sugar levels. Always follow their instructions and monitor blood sugar as advised.
10. Blood sugar monitoring
Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as directed by your healthcare provider. Keeping track of your levels will help you and your medical team adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
11. Manage stress
High levels of stress can affect blood sugar levels. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or prenatal yoga to help manage stress.
12. Get enough sleep
Prioritize getting adequate rest, as sleep deprivation can influence blood sugar levels.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends a history of gestational diabetes test for type 2 diabetes every one to three years after their preliminary post-pregnancy test for diabetes should be done. It is also suggested to work with the doctor to eat healthily, lose excess weight, and exercise regularly to maintain blood sugar levels in pregnancy and decrease the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
References
1. Moon, J. H., & Jang, H. C. (2022). Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications. Diabetes & Metabolism Journal,
2. Quintanilla, B. S., & Mahdy, H. (2019, July 28). Gestational diabetes. National Library of Medicine; StatPearls Publishing.
Tags
Blood Sugar Levels in Pregnancy: What You Should Know in Tamil



Written by
Priyanka Verma
Priyanka is an experienced editor & content writer with great attention to detail. Mother to an 11-year-old, she's a ski
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Questions
Hello frnds..still no pain...doctor said head fix nhi hua hai..bt vagina me pain hai aur back pain bhi... anyone having same issues??

Kon kon c chije aisi hai jo pregnancy mei gas acidity jalan karti hain... Koi btayega plz bcz mujhe aksar khane ke baad hi samagh aata hai ki is chij se gas acidity jalan ho gyi hai. Please share your knowledge

I am 13 week pregnancy. Anyone having Storione-xt tablet. It better to have morning or night ???

Hlo to be moms....i hv a query...in my 9.5 wk i feel body joint pain like in ankle, knee, wrist, shoulder, toes....pain intensity is high...i cnt sleep....what should i do pls help....cn i cosult my doc.

Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers | laundry detergent 6472 | lactomama lactation granules |