Home

PCOS & PCOD

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
In this Article

PCOS & PCOD
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Updated on 3 November 2023
Sitting in the doctor's office, Garvita’s mind was a whirlwind of emotions as she heard the words "Polycystic Ovary Syndrome" for the first time. She was suddenly thrust into a world of medical jargon and unfamiliar territory. Like many women facing this unexpected diagnosis, she was left wondering, "What is PCOS, and why me?"
As she began to unravel the mysteries of this condition, she realized she was not alone on this journey. PCOS affects millions of women worldwide, yet its complexities often remain shrouded in misconceptions. So, join Garvita as we explore the origins of PCOS to the telltale signs that set it apart and shed light on its possible treatment options.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
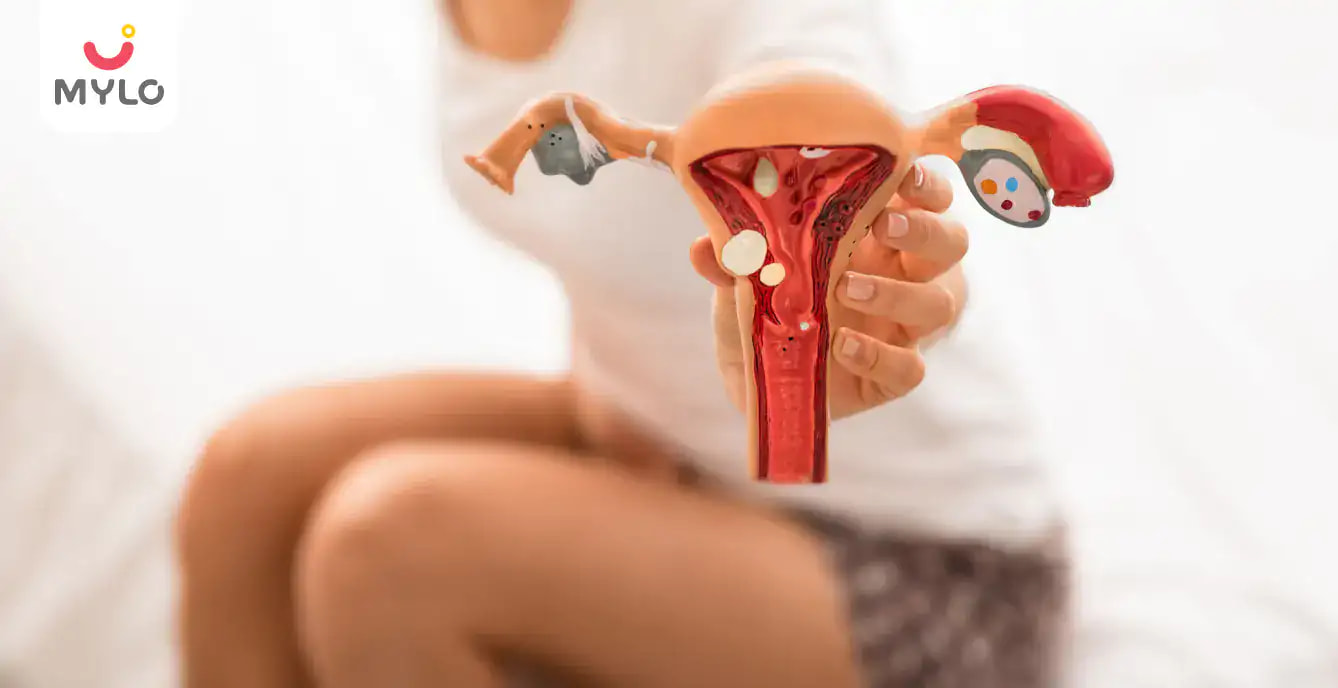
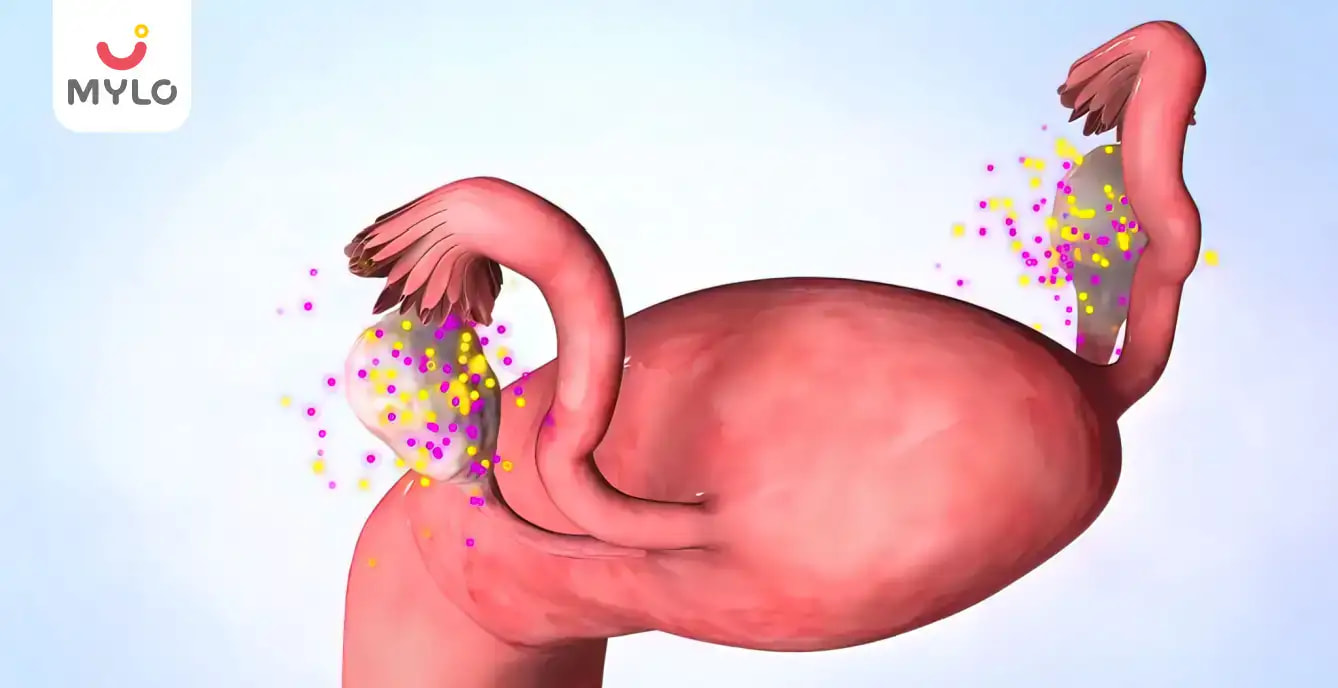
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by enlarged ovaries containing small fluid-filled sacs called cysts. Women with PCOS may experience hormonal imbalances, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and difficulties with ovulation. Proper diagnosis and management are essential to address the symptoms and potential long-term health implications of PCOS.
How does PCOS affect women's reproductive health?
PCOS can significantly impact women's reproductive health in various ways:
1. Menstrual Irregularities
Women with PCOS often experience irregular menstrual cycles or may even skip periods due to hormonal imbalances. This can make it difficult to predict ovulation and plan for pregnancy.
2. Infertility
The lack of regular ovulation can lead to difficulties in conceiving, making PCOS one of the leading causes of infertility in women.
3. Ovarian Cysts
PCOS is characterized by enlarged ovaries containing multiple small fluid-filled cysts. These cysts can interfere with the normal release of eggs during ovulation.
4. Hormonal Imbalances
Women with PCOS may have higher levels of androgens (male hormones) than usual, leading to symptoms like acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and male pattern baldness.
5. Insulin Resistance
Many women with PCOS also experience insulin resistance, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
6. Weight Gain
PCOS is often associated with weight gain or difficulty losing weight, which can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance.
7. Pregnancy Complications
Women with PCOS may have a higher risk of certain pregnancy complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and premature birth.
8. Long-Term Health Implications
PCOS is also associated with an increased risk of developing other health conditions later in life, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and endometrial cancer.
Regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare professionals specializing in PCOS can help women manage the condition and improve their overall reproductive health.
PCOS Symptoms
-
PCOS symptoms include irregular periods, excess hair growth, and hormonal imbalances.
-
Women with PCOS may experience weight gain, acne, and difficulty getting pregnant.
-
PCOS can cause insulin resistance, ovarian cysts, and long-term health risks.
-
Hormonal imbalances in PCOS can lead to excessive androgen levels and male pattern hair loss.
-
Infertility and menstrual irregularities are common features of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
PCOS Causes
The precise cause of PCOS remains unknown, but genetics is believed to be a contributing factor. Additionally, several other elements, notably obesity, are involved in its development:
1. Elevated Androgen Levels
Higher androgen levels can hinder ovulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and the formation of fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries. Androgen excess also causes acne and excessive hair growth in women and individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB).
2. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance prompts the ovaries to produce and release more androgens, contributing to PCOS symptoms. Insulin aids in processing glucose for energy, but resistance means that glucose remains high in the blood. Overweight or obesity can exacerbate insulin resistance, and high insulin levels, even with normal blood glucose, may indicate it.
3. Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation
People with PCOS often experience ongoing low-grade inflammation. Blood tests measuring C-reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cells can assess the body's inflammatory state.
Types of PCOS
Types of PCOS are given below:
1. Insulin-Resistant PCOS
This type is associated with insulin resistance, where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to higher insulin levels.
2. Non-Insulin-Resistant PCOS
In this type, insulin resistance is not a prominent feature, and hormonal imbalances primarily contribute to PCOS symptoms.
3. Post-Pill PCOS
Some women may develop PCOS-like symptoms after discontinuing certain hormonal contraceptives, which can disrupt the normal hormonal balance.
4. Inflammatory PCOS
This type involves chronic inflammation in the body, leading to hormonal imbalances and PCOS symptoms.
You may also like : PCOD Vs. PCOS: What's the Difference?
PCOS Diagnostic Criteria
The PCOS diagnostic criteria, as established by the Rotterdam criteria, require the presence of at least two out of three key features:
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
Evidence of irregular or absent menstrual cycles due to irregular ovulation.
2. Clinical or Biochemical Signs of Hyperandrogenism
This includes symptoms like hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and male pattern hair loss, along with elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) in blood tests.
3. Polycystic Ovaries
The presence of multiple small fluid-filled cysts in the ovaries observed through ultrasound.
Other conditions must be ruled out before confirming a PCOS diagnosis. These criteria help healthcare professionals in identifying and managing PCOS effectively.
You may also like : PCOS Tea: A Warm Cup of Tea to Help You Keep PCOS at Bay
PCOS Treatment
The PCOS treatment is focused on managing symptoms and addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances. It involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and achieving a healthy weight can help improve insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance.
2. Insulin-Sensitizing Medications
Medications like Metformin can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels in some women with PCOS.
3. Clomiphene citrate (Clomid)
This drug stimulates ovulation and is commonly used for infertility treatment, often in combination with metformin.
4. Letrozole (Femara)
An ovulation inducer, Femara is increasingly used to address ovulation issues, especially in women with PCOS. It can also be used alongside metformin to enhance the chances of successful conception.
5. Hormone shots
Injectable fertility drugs may be recommended if Clomid or Femara, with or without metformin, do not yield desired results.
6. IVF (In Vitro Fertilization)
If other treatments prove ineffective, IVF can be considered to achieve pregnancy for women with PCOS
7. Ovarian drilling
This surgical procedure involves using a thin needle to burn small areas of the ovaries, aiming to lower the production of male hormones and improve ovulation. Results from ovarian drilling are inconsistent, and not all practitioners recommend it as a PCOS treatment
8. Endometrial Protection
To counter the increased risk of endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the uterine lining) in women with irregular periods, progestin therapy may be recommended.
9. Natural Herbal remedies
One can also leverage the benefits of natural ingredients like Shatavari, Manjistha, Shankh Pushpi, chamomile, Myo-inositol, Vit D, and quatre folic. These natural ingredients help to combat insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and stress related to the condition. You can also try Mylo’s PCOD/PCOS tea and Myo-inositol chewable tablets to combat PCOS and PCOD symptoms and maintain your ovarian health.
Final Thoughts
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a complex hormonal disorder that can significantly impact women's reproductive health and overall well-being. It is essential for women with PCOS to seek timely diagnosis, engage in proactive management, and work closely with healthcare professionals to address symptoms and potential long-term health implications. Lifestyle modifications, medication, and fertility treatments can play a pivotal role in improving quality of life and increasing the chances of successful pregnancies for women with PCOS.
Tags: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Treatment, Management in Telugu, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Treatment, Management in Bengali, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Treatment, Management in Hindi
References
1. I, L., & Mayrin, J. V. (2018, November 18). Polycystic Ovarian Disease (Stein-Leventhal Syndrome). Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing.
2. Sadeghi, H. M., Adeli, I., Calina, D., Docea, A. O., Mousavi, T., Daniali, M., Nikfar, S., Tsatsakis, A., & Abdollahi, M. (2022). Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of Pathogenesis, Management, and Drug Repurposing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences



Written by
Mittali Khurana
Mittali is a content writer by profession. She is a dynamic writer with 04+ years of experience in content writing for E-commerce, Parenting App & Websites, SEO.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Questions
Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Hai.... My last period was in feb 24. I tested in 40 th day morning 3:30 .. That is faint line .. I conculed mylo thz app also.... And I asked tha dr wait for 3 to 5 days ... Im also waiting ... Then I test today 4:15 test is sooooo faint ... And I feel in ma body no pregnancy symptoms. What can I do .

Baby kicks KB Marta hai Plz tell mi

PCOD kya hota hai

How to detect pcos

RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |