Home

Illnesses & Infections

Malabsorption Syndrome: Types, Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
In this Article
Illnesses & Infections
Malabsorption Syndrome: Types, Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
Updated on 23 May 2023
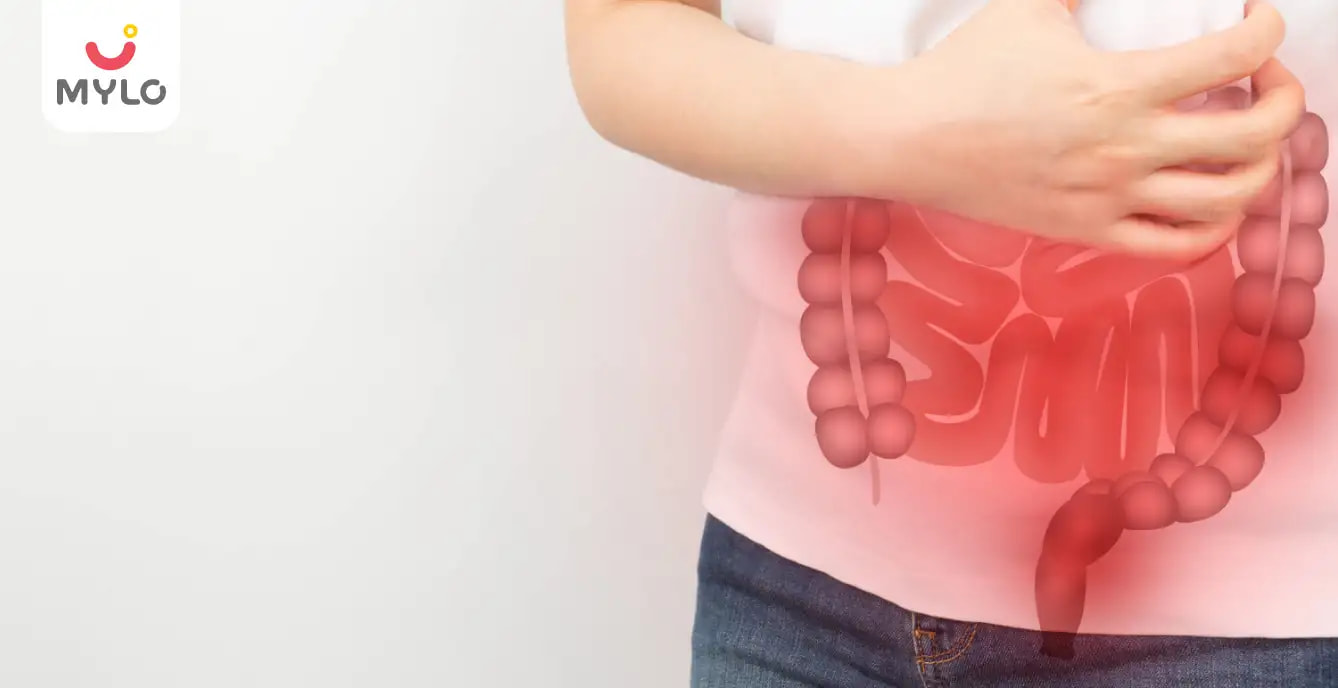
The human body needs nutrients to facilitate repair, growth and perform different life processes. Herein, the small intestine plays an integral role in absorbing nutrients. However, sometimes the body cannot absorb certain macro and micronutrients, leading to malabsorption. Several causes can lead to the condition, including damage to the small intestine lining and more.
This article elaborates on the malabsorption syndrome definition, its causes, symptoms and treatment.
What is malabsorption?
Malabsorption is caused due to the body's inability to absorb nutrients from food in the small intestine or colon. Instead, the unabsorbed nutrients get eliminated in faeces. They may have a variety of causes ranging from enzyme deficiencies, damage of the lining in the small intestine, a side-effect of medications, cystic fibrosis, etc.
What happens if you suffer from malabsorption?
Malabsorption affects the body's ability to absorb all or specific nutrients thrown out in stools. Individuals with malabsorption syndrome often experience side effects like diarrhoea or gastrointestinal distress, leading to fast moving out of food through the bowels and obstructing the absorption of nutrients.
Over time, the patient may show malabsorption symptoms of nutrient deficiency, including macronutrients (protein, fats, carbohydrates) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Lack of these nutrients may affect eyes, skin, bones and hair in addition to conditions like muscle atrophy and reduced immunity.
Types of malabsorption disorders
The form of malabsorption depends mainly on the nutrients the body cannot absorb. These include:
1. General malabsorption:
Gastrointestinal diseases like inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease are common malabsorption syndrome causes.
2. Fat malabsorption
occurs when the small intestine cannot absorb fats and pass them to the colon, causing Steatorrhea (fatty stools). It also causes fat-soluble vitamins like A, E, D, and K malabsorption.
3. Carbohydrate malabsorption:
Occurs in people sensitive to sugars causing gas pain and abdominal bloating. Herein, the carbohydrates are not fully absorbed in the small intestine and cause bacteria fermentation in the colon that breaks down into short-chain fatty acids and gasses.
4. Protein malabsorption:
Occurs in people with gluten or milk protein intolerance
5. Bile acid malabsorption:
Results due to lack of bile from diseases of bile ducts, liver or gall bladder, often causing chronic diarrhoea.
Symptoms of malabsorption syndrome
It is important to note that the symptoms of malabsorption may differ according to the nutrients, such as proteins, vitamins, sugars and fats that are not absorbed. These include:
- Hair loss
- Dry hair
- Fluid retention leading to oedema
- Anaemia
- Low blood pressure
- Malnutrition
- Bone pain, tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Weight loss
- Muscle wasting
- Steatorrhea or fatty stools
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain and distension in the stomach
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhoea
- A weight that is below children of similar age
- Amenorrhea
- Delay in development.
- Apathy or irritability
Causes of malabsorption syndrome
The most common malabsorption causes include:
- Cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder affecting the pancreas leading to digestive issues and absorption of nutrients
- Celiac disease, an autoimmune issue impacting the small intestine
- Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel issue damaging to the small intestine
- Overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine and Giardiasis damaging the small intestine
- Medications: intake of proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics
- Removal of a part of the small intestine
- Overproduction of acid in the stomach, such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy
- Over usage of alcohol
- Inability to break digestive enzymes due to conditions like pancreatic insufficiency, bile duct blockages, gallbladder or liver diseases
- Lymphatic disorders causing blocking of vessels, such as lymphoma and lymphangiectasia
- Lactose intolerance
Risks of malabsorption syndrome
Malabsorption syndrome occurs due to the body's inability to absorb nutrients from food. The risk factors include:
- Malnutrition
- Inability to gain weight
- Diarrhoea
- Anaemia
- Frequent infections
- Damage to nerves
- Osteoporosis
It may also increase the risk of developing specific mineral and vitamin deficiencies like vitamin B12, vitamin D and iron. In severe cases, it leads to organ damage and can threaten life.
How can one determine whether they have malabsorption?
The healthcare provider may evaluate malabsorption syndrome by examining a few symptoms, diagnosing the process, and asking questions about health history. They will check for symptoms like chronic diarrhoea, anaemia, muscle wastage, fatty stools, and malnutrition.
Based on the symptoms of malabsorption, the medical professional will suggest appropriate tests to confirm the condition.
Which tests are performed to diagnose malabsorption?
There are several invasive and non-invasive tests performed to diagnose malabsorption syndrome, which include:
- Stool tests to check for undigested vitamins, fats, or other substances
- Blood tests to check for anaemia, low levels of proteins, and high levels of certain fats
- Imaging tests like X-ray, CT scan, endoscopic ultrasound, or video capsule endoscopy to check for blockages or abnormalities in the intestinal tract
- Intestinal biopsy to check damage to villi in the small intestine by taking a small tissue sample
- Sweat test to check for cystic fibrosis
- Faecal elastase test to check exocrine pancreatic function
- The lactose tolerance test checks the level of lactose intolerance
- Gastric emptying test to check if food is moving properly through the small intestine and stomach
- Breath tests hydrogen breath test to detect intolerance to specific carbohydrates
Treatment for malabsorption syndrome
Malabsorption treatment will depend on the underlying reason. Common treatments include:
The doctor may suggest medicines like loperamide to manage symptoms like stomach pain and diarrhoea
- Change in diet including increased intake of certain nutrients like B12, vitamin D, and iron in addition to lactose-free food
- Enzyme replacement therapy
- Supplements for vitamins and minerals
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy
- Removal of abnormal growth and blockages through surgery
Can malabsorption go away?
Malabsorption is a chronic condition that may not go away entirely. However, it can be controlled by proper malabsorption treatments to reduce symptoms. If the underlying reason for the condition is parasite infection or celiac disease, it can be resolved. However, in the case of conditions like cystic fibrosis or genetic disorders, they cannot be cured.
FAQs
1. What is the main cause of malabsorption?
Malabsorption may be temporarily caused due to stomach flu. Other causes of malabsorption syndrome include damage of the lining in the small intestine, pancreas, liver or gallbladder diseases, lymphatic diseases, or intolerance to certain foods.
2. What does the poop look like with malabsorption?
Malabsorption stool appears bulky, greasy, and loose, accompanied by a foul smell.
3. Which symptom is the classic symptom of malabsorption?
Chronic diarrhoea is a classic symptom of malabsorption followed by Steatorrhea.
4. What happens if malabsorption goes untreated?
If left untreated, the patient may show signs of undernutrition, including reduced immunity and muscle wasting.



Written by
Ishmeet Kaur
Ishmeet is an experienced content writer with a demonstrated history of working in the internet industry. She is skilled in Editing, Public Speaking, Blogging, Creative Writing, and Social Media.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
What Power Pumping Schedule Works Best To Increase Breast Milk Supply?
Which Diaper Ingredients Should You Avoid For Sensitive Skin Babies?
Which Organic Disposable Diapers Are Safest for Newborns with Sensitive Skin in India?
How to Understand Diaper Price Range in India and Compare Cost per Diaper Before You Buy Online
Related Questions
Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Hai.... My last period was in feb 24. I tested in 40 th day morning 3:30 .. That is faint line .. I conculed mylo thz app also.... And I asked tha dr wait for 3 to 5 days ... Im also waiting ... Then I test today 4:15 test is sooooo faint ... And I feel in ma body no pregnancy symptoms. What can I do .

Baby kicks KB Marta hai Plz tell mi

PCOD kya hota hai

How to detect pcos

RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Care for Baby
Top 10 Short Bedtime Stories for Kids
Pregnancy Complications
RH Incompatibility in Pregnancy - Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Symptoms & Illnesses
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Symptoms & Treatment
Care for Baby
Why Babies Cry After Birth?
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF Process Step by Step Timeline: What to Expect During Your Fertility Journey
Symptoms & Illnesses
Tracheoesophageal Fistula: Causes, Symptoms, Risks & Treatment
- Stillbirth: Cause, Symptoms, Risks & Prevention
- Giant Congenital Melanocytic Nevus: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
- Tokophobia: How to Manage Your Phobia of Pregnancy & Childbirth
- Low BP in Pregnancy: Symptoms, Effects & Treatments
- Helping your twins to sleep at the same time
- Baby Brain Development: What You Should Know
- Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty) Procedure, Risks, Preparation & Recovery
- Spina Bifida: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
- Diastasis Recti: Causes, Symptoms, Risks & Preventions
- Opioid Overdose, Risk & Prevention
- Is Pregnancy After 35 Right for You? A Comprehensive Guide
- Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus): Meaning, Symptoms & More
- RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
- Loose Vagina: Learn How To Tighten Your Vagina Naturally


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |




