Home

PCOS & PCOD

Bilateral PCOD Explained: Meaning, Symptoms, and Effective Management
In this Article

PCOS & PCOD
Bilateral PCOD Explained: Meaning, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Updated on 6 October 2023



Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Shruti Tanwar
C-section & gynae problems - MBBS| MS (OBS & Gynae)
View Profile

Are you facing irregular menstrual periods, acne, excessive hair growth, or infertility issues? You might be dealing with bilateral PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease), a condition that affects women's ovaries and hormone production. In this article, we will delve into the meaning, symptoms, and effective management strategies for bilateral polycystic ovaries.
While there is no exact cure, there are ways to control and manage the symptoms through lifestyle changes, diet, and exercise. Discover how you can take charge of your health and improve your overall well-being in the face of this challenging condition.
What is Bilateral Polycystic Ovaries?
Bilateral Polycystic Ovaries is a condition that affects the ovaries, causing multiple small cysts to develop. This condition is characterized by an imbalance in hormone levels, particularly an increase in androgens, which are male hormones. As a result, the ovaries are unable to release eggs regularly, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and difficulties in conceiving.
What is the Difference Between Bilateral PCOD and Bilateral PCOS?
Bilateral PCOD and Bilateral Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. While both conditions involve the development of multiple cysts on the ovaries, bilateral PCOS means a broader term that encompasses not only the cysts but also other symptoms such as irregular periods, hormonal imbalances, and potential complications like insulin resistance.
When it comes to what is bilateral PCOD, it refers specifically to the presence of cysts on both ovaries.
You may also like : PCOD Diet: How the Right Diet Can Transform Your Life
Symptoms
Let us take a look at the tell-tale signs of this condition:
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
Women with this condition often experience irregular periods, which may be infrequent, heavy, or prolonged.
2. Excessive Hair Growth
Increased androgen levels can lead to hirsutism, which is the growth of excessive hair on the face, chest, and other areas of the body.
3. Acne
Hormonal imbalances can cause persistent acne breakouts.
4. Weight Gain
Many women struggle with weight gain or find it difficult to lose weight.
5. Mood Changes
Fluctuating hormone levels can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and depression.
6. Fatigue
Women may also experience persistent fatigue and low energy levels.
7. Infertility
Difficulties in conceiving are common in women due to irregular ovulation.
You may also like: PCOS with Regular Periods: Understanding the Symptoms and Implications
Causes
Now that we know what is bilateral polycystic ovaries, it is important to understand its causes as well:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
The exact cause of is not fully understood; however, hormonal imbalances, particularly increased androgen levels, play a significant role.
2. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, is commonly associated with this condition.
3. Genetics
There is evidence to suggest that certain genetic factors may contribute to the development of bilateral polycystic ovaries.
4. Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation in the body may be linked to this condition.
5. Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental toxins and endocrine disruptors may increase the risk of developing this condition.
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Morphology
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Morphology refers to the physical characteristics of the ovaries in individuals with bilateral PCOD. The ovaries may appear enlarged and contain multiple small cysts, which are typically less than 10mm in size. This morphology is often identified through ultrasound imaging.
It is important to note that the presence of cysts alone does not necessarily indicate bilateral PCOD, as other factors, such as hormonal imbalances and irregular periods, must also be considered for an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment and Management of Bilateral PCOD
The treatment for bilateral polycystic ovaries usually involves a combination of medications, surgical interventions, supplements and natural remedies. Let us take a look at some effective management techniques:
1. Birth control and anti-androgen pills
Oral contraceptives are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Anti-androgen medications may also be used to counteract the effects of increased androgens.
2. Ovarian drilling
In some instances, surgical procedures such as ovarian drilling or ovarian wedge resection may be recommended to improve fertility outcomes.
3. Inositol supplements
Inositol, a B-vitamin-like compound, has shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity and regulating menstrual cycles. It can be found in two forms: myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, which have both proven beneficial for women with PCOS/PCOD.
Myo-inositol has especially been found to improve insulin sensitivity, restoring menstrual regularity, reducing androgen levels and improving fertility. You can also consider Mylo's chewable Myo-inositol tablets, which are fortified with Quatre Folic and Vitamin D and can help promote hormonal balance and overcome common as well as specific PCOS/PCOD challenges.
4. Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have also been associated with reduced inflammation and improved hormonal balance.
5. Herbal teas
Replacing carbonated, sugary drinks and milk teas with herbal teas like PCOS/PCOD Tea can also be a great way to manage bilateral polycystic ovaries. These herbal teas should include ingredients like cinnamon, chamomile, fennel, fenugreek, Shatavari, Manjishtha, Amla, Shankhpushpi etc.
Mylo offers herbal solutions to combat the symptoms associated with PCOD like weight gain, acne, irregular periods, and mood swings. Mylo’s PCOD tea, which contains potent ingredients like cinnamon, chamomile, fennel, fenugreek, Shatavari, Manjishtha, Amla, Shankhpushpi can also help you manage these symptoms.
6. Lifestyle changes
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and sufficient sleep may help regulate hormone levels and improve overall well-being.
FAQs
1. Is bilateral polycystic ovaries normal?
The presence of polycystic ovaries is relatively common, with estimates suggesting that up to 20% of women may have this characteristic on ultrasound.
2. Can I get pregnant with bilateral polycystic ovaries?
Many women with this condition are still able to become pregnant. Treatment options, such as medications and assisted reproductive techniques, can help improve fertility outcomes.
3. How do you treat bilateral polycystic ovaries naturally?
Management involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress reduction, and sufficient sleep. Certain supplements, such as myo-inositol and omega-3 fatty acids, may also provide additional support.
Final Thoughts
Bilateral PCOD is a complex condition that affects many women worldwide. While there is no cure for this condition, effective management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve fertility outcomes. A combination of medications, surgical interventions, supplements, and lifestyle changes can contribute to better hormonal balance and overall well-being. It is crucial for individuals to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs.
References
1. Ferriman D. (1960). Bilateral Polycystic Ovaries. Postgrad Med J.
2. Rosenfield RL. (2015). The Polycystic Ovary Morphology-Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Spectrum. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol.





Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Shruti Tanwar
C-section & gynae problems - MBBS| MS (OBS & Gynae)
View Profile


Written by
Anupama Chadha
Anupama Chadha, born and raised in Delhi is a content writer who has written extensively for industries such as HR, Healthcare, Finance, Retail and Tech.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Top 100 Baby Names for Boys and Girls 2026 Edition: The Ultimate Trending & Meaningful Name Guide
The Ultimate Guide to the Best Romantic Web Series on OTT for Couples
Best Indian Crime Web Series Based on True Stories: The Ultimate Binge-Watch Guide (2026)
Dark & Suspenseful OTT Shows You Can’t Stop Watching: The 2026 Binge List
Related Questions
Hello frnds..still no pain...doctor said head fix nhi hua hai..bt vagina me pain hai aur back pain bhi... anyone having same issues??

Kon kon c chije aisi hai jo pregnancy mei gas acidity jalan karti hain... Koi btayega plz bcz mujhe aksar khane ke baad hi samagh aata hai ki is chij se gas acidity jalan ho gyi hai. Please share your knowledge

I am 13 week pregnancy. Anyone having Storione-xt tablet. It better to have morning or night ???

Hlo to be moms....i hv a query...in my 9.5 wk i feel body joint pain like in ankle, knee, wrist, shoulder, toes....pain intensity is high...i cnt sleep....what should i do pls help....cn i cosult my doc.

Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Vaginal Discharge
Early Pregnancy & Egg White Discharge: What You Need to Know
Abortion
Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Procedure, Risks & Benefits

Reproductive health
Alivher Tablet Uses: How to Maximize the Benefits for Your Reproductive Health
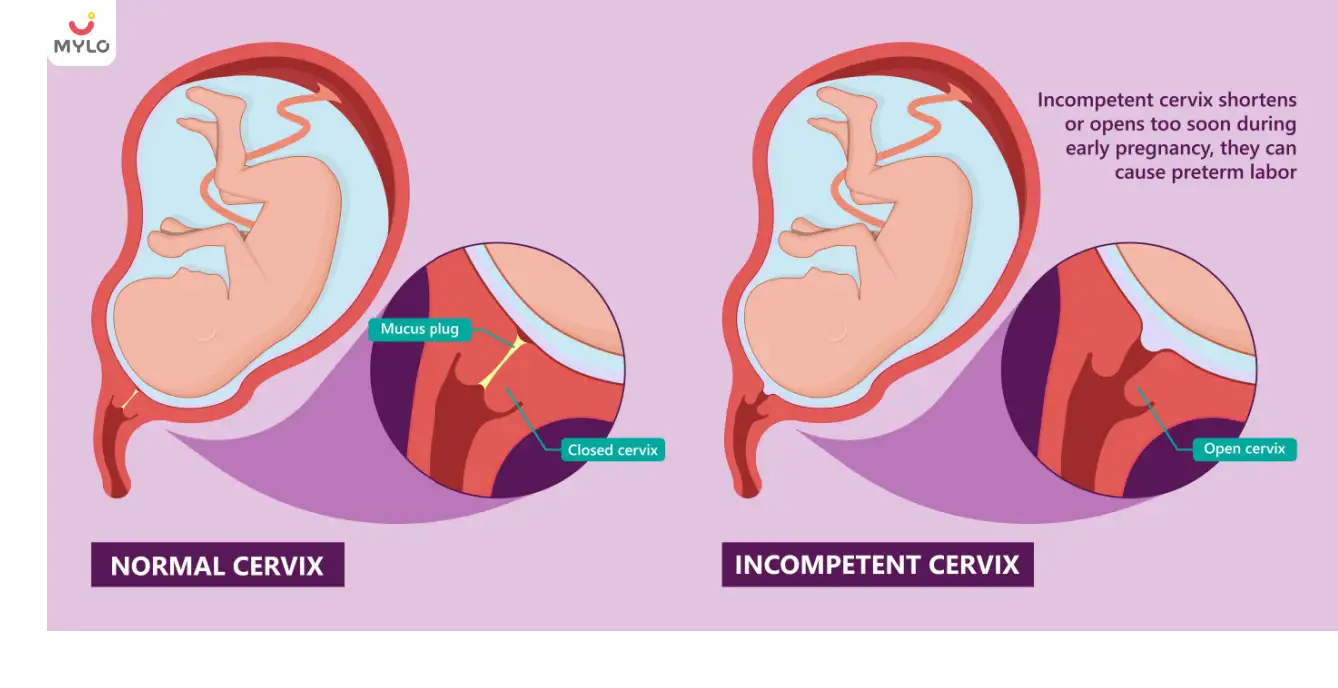
Preterm Labour
Incompetent cervix: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment

Pregnancy Precautions
Soda During Pregnancy: Is It Safe or Should You Avoid It?

Vaginal Discharge
Watery Discharge Before Period: Is It Normal or a Cause for Concern
- Sperm Cramps: Debunking Myths and Shedding Light on the Facts
- Bitter Gourd During Pregnancy: Benefits and Precautions You Should Know
- First Period After Failed IVF Cycle: What to Expect and How to Cope
- Freezing Eggs: The Pros and Cons of Preserving Your Fertility
- Can a Diabetic Woman Get Pregnant: Exploring the Facts and Myths
- Bulky Uterus with Fibroids: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Tubal Recanalization: How This Procedure Can Help Restore Your Fertility
- Are FSH (Urofollitropin) Injections an Effective and Safe Fertility Treatment For You?
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing a Baby Massage Oil for Summer
- The Ultimate Guide to Understanding a Follicle Size Growth Chart
- Fruits for PCOS: Your Guide to Making Healthy Choices
- Is Milk Good for PCOS: Exploring the Dairy Dilemma
- The Ultimate Guide to Using Ashokarishta for PCOS
- PCOS Pain: The Ultimate Guide to Causes and Effective Management


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |




