Home

Prenatal Tests

Thalassemia Test in Pregnancy: The Ultimate Guide for Expecting Parents
In this Article
Prenatal Tests
Thalassemia Test in Pregnancy: The Ultimate Guide for Expecting Parents
Updated on 3 November 2023
As expecting parents, you eagerly prepare for every aspect of your baby's arrival, from choosing the perfect name to creating a cozy nursery. However, amidst the excitement and dreams, it's crucial to address another essential aspect of parenthood – your child's health. One of the first steps in ensuring a healthy start for your baby is understanding the factors that may affect their well-being.
Thalassemia, a group of inherited blood disorders, is one such factor that can significantly impact your child's life. In this article, we will understand the importance of thalassemia test in pregnancy, different types of screenings tests available and steps to take to ensure a safe future for your baby.
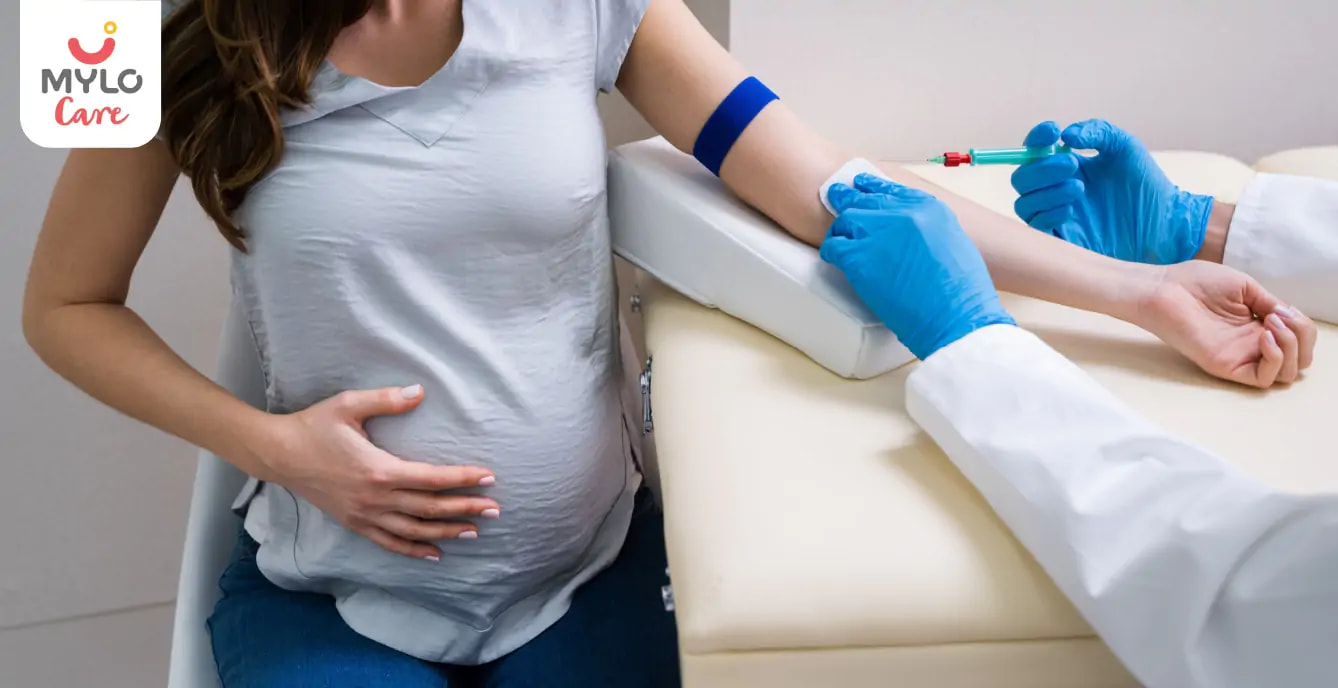
What is the importance of thalassemia blood test during pregnancy?
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood. It can be passed on from parents to their children, and thalassemia testing in pregnancy allows healthcare providers to identify if the mother is a carrier of thalassemia or if the baby has inherited the disorder.
This information helps in determining the risk of the baby developing thalassemia major, a severe form of the disorder. By detecting thalassemia early on, parents can take necessary precautions and seek appropriate medical care to ensure the well-being of their child.
You may also like: What Are the Common Tests You Will Have During Your Pregnancy?
Thalassemia carriers and their implications for the baby
If one or both parents are carriers of thalassemia in pregnancy, there is a risk that the baby may inherit the disorder. The implications for the baby can vary depending on various factors, such as the specific type of thalassemia and the severity of the parents' condition.
If both parents are carriers of thalassemia, there is a higher chance of the baby being affected by the disorder. The severity of thalassemia can range from mild to severe, with thalassemia major being the most severe form. Thalassemia major requires lifelong treatment and medical care. If only one parent is a carrier, the baby may inherit the carrier status without having the disorder.
You may also like: The Scans Required at the End of Second Trimester of Your Pregnancy
Types of thalassemia screening test in pregnancy
Thalassemia screening during pregnancy is essential to identify whether the expecting parents are carriers of thalassemia genes. These tests help determine the risk of having a child with thalassemia major or intermedia. There are a few different types of screening tests that can detect thalassemia in pregnancy:
1. Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This is a routine blood test that measures the different components of blood, including hemoglobin levels. Low hemoglobin levels may indicate the presence of thalassemia.
2. Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
This test separates different types of hemoglobin in the blood, allowing for the detection of abnormal hemoglobin patterns associated with thalassemia.
3. Hemoglobin HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography)
This is a more advanced and precise method for detecting abnormal hemoglobin variants, including those associated with thalassemia.
4. Molecular DNA Testing
This is the most definitive test for thalassemia and can identify specific genetic mutations associated with the condition. It can determine if an individual is a carrier or if the fetus has inherited thalassemia genes from both parents.
5. Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
If the parents are known carriers of thalassemia or if there is a high risk of the fetus having thalassemia, these invasive tests can be performed during pregnancy to directly assess the baby's DNA for thalassemia mutations.
What are the risks associated with thalassemia test in pregnancy?
Thalassemia tests during pregnancy are generally safe and are crucial for identifying carriers of thalassemia genes. However, like any medical procedure, there are some potential risks associated with thalassemia testing in pregnancy including:
1. False Positives or False Negatives
Thalassemia screening tests can sometimes produce false positive or false negative results. A false positive may cause unnecessary anxiety and additional testing, while a false negative might lead to the incorrect assumption that the fetus is not at risk when it actually is.
2. Anxiety and Emotional Distress
The process of undergoing thalassemia testing, particularly more invasive tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), can be stressful and emotionally taxing for expecting parents. The waiting period for results and the possibility of adverse findings can cause anxiety and emotional distress.
3. Invasive Procedures
Invasive diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis and CVS, carry a small risk of miscarriage (typically less than 1%) due to the insertion of a needle or catheter into the amniotic sac or placenta. While the risk is low, it's essential to consider it when deciding to undergo these procedures.
4. Infection
Any invasive medical procedure carries a slight risk of infection, including thalassemia tests like amniocentesis or CVS. Healthcare providers take precautions to minimize this risk, such as using sterile equipment, but there is always a minimal chance of infection.
5. Bleeding or Injury
During invasive tests like amniocentesis or CVS, there is a small risk of bleeding or injury to the fetus, amniotic sac, or placenta. These complications are rare but can potentially harm the pregnancy.
How to interpret the results of thalassemia blood test?
Interpreting the results of a thalassemia test can be complex. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can accurately analyze the results and provide appropriate guidance. Here are a few possible scenarios and their interpretations:
1. Negative Result
A negative result indicates that the mother is not a carrier of thalassemia and the baby has not inherited the disorder. However, it's important to note that there is still a small chance of being a carrier, especially if there is a family history of thalassemia.
2. Positive Result
A positive result implies that the mother is a carrier of thalassemia, but it does not confirm if the baby has inherited the disorder. Further testing, such as DNA analysis, may be required to determine the baby's condition accurately.
3. Inconclusive Result
In some cases, the test results may be inconclusive, indicating the need for additional testing or a retest. This can be due to various factors, such as technical issues or the presence of other genetic variations.
It is crucial to discuss the test results with a healthcare provider who can provide personalized guidance based on the specific circumstances.
You may also like: Why is the Second Trimester Anomaly Scan Important During Pregnancy?
What to do if the results are positive?
If the thalassemia test results are positive, indicating that the mother is a carrier of thalassemia in pregnancy, further steps can be taken to ensure the well-being of the baby. Here are a few important considerations:
1. Consult a Genetic Counselor
A genetic counselor specializes in assessing the risk and implications of genetic disorders. They can provide detailed information about thalassemia, its inheritance patterns, and the probability of the baby being affected.
2. Prenatal Diagnosis
Depending on the severity of thalassemia and the couple's preferences, further prenatal testing may be recommended. These tests can provide a more definitive diagnosis and help parents make informed decisions about the pregnancy.
3. Plan for Treatment
If the baby is diagnosed with thalassemia, it is essential to plan for appropriate treatment and care. This may involve regular blood transfusions, medication, and close monitoring by a specialized healthcare team.
You may also like: Fetal Echo Test in Pregnancy: A Diagnostic Tool for Detecting Heart Defects in the Womb
The Bottomline
Thalassemia test in pregnancy is crucial for expecting parents to ensure the well-being of their baby. By identifying carriers and detecting the disorder early on, parents can make informed decisions about treatment options and provide the necessary care for their child.
References
1. Ghosh S, Chakrabarti S, Bhattacharyya M. (2021). Prenatal Screening and Diagnosis of ß-Thalassemia in India: Is ARMS-PCR Enough? Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus.
2. Leung TN, Lau TK, Chung TKh. (2005). Thalassaemia screening in pregnancy. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol.
Tags
Thalassemia Test in Pregnancy in Bengali, Thalassemia Test in Pregnancy in Tamil, Thalassemia Test in Pregnancy in Telugu



Written by
Madhavi Gupta
Dr. Madhavi Gupta is an accomplished Ayurvedic doctor specializing in Medical content writing with an experience of over 10 years.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |