Home

Postnatal Care

Postpartum Thyroiditis: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
In this Article

Postnatal Care
Postpartum Thyroiditis: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Updated on 3 November 2023
What is postpartum thyroiditis?
After giving birth, many women experience a condition known as postpartum thyroiditis. This condition occurs when the thyroid gland, located in the neck, becomes inflamed. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland that produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolism.
Postpartum thyroiditis is classified into two types: subclinical and clinical. When there are no symptoms of thyroiditis but blood tests show that the thyroid is not functioning normally, this is referred to as subclinical thyroiditis. Thyroiditis becomes clinical when there are symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, depression, and anxiety.
The exact cause of postpartum thyroiditis is not very clear, but it is thought to be related to the changes in hormone levels that occur after pregnancy. Postpartum thyroiditis treatment typically involves levothyroxine, a medication that replaces the thyroid hormone.
Who is at risk for postpartum thyroiditis?
According to studies, Postpartum thyroiditis affects about 8% of all pregnancies. It can occur both before and after pregnancy, but it is more likely to occur in women with a family history of thyroid disease and when the mother is older. Certain autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis are at higher risk of postpartum thyroiditis.
Furthermore, women who are antithyroid peroxidase antibody positive for Hashimoto's thyroiditis before becoming pregnant have a greater risk of developing postpartum thyroiditis. Postpartum thyroiditis occurs most frequently within the first three months following delivery. However, the majority of postpartum thyroiditis cases occur within the first month postpartum.
What causes postpartum thyroiditis?
Postpartum thyroiditis is a condition that can occur after pregnancy. It is characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland and can cause symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
The exact cause of postpartum thyroiditis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to the changes in hormone levels that occur during pregnancy and after childbirth. It is more common in women who have a history of thyroid problems, such as Graves' disease or Hashimoto's disease.
Postpartum thyroiditis usually resolves on its own within a few months. However, if the condition is severe, treatment with thyroid hormone replacement may be necessary.
What are the symptoms of postpartum thyroiditis?
The postpartum thyroiditis symptoms can vary depending on whether the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive. If the thyroid gland is overactive, it may experience symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and weight loss. If the thyroid gland is underactive, it may experience symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and weight gain.
Postpartum thyroiditis symptoms usually go away on their own within a few months. However, in some cases, the condition can become permanent. If someone has postpartum thyroiditis, it is important to see the doctor for treatment
Symptoms of Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- Enlarged/swelled thyroid gland
- Heart palpitations
- Weight loss
- Anxiety
- Weight gain
- Heat sensitivity
- Twitching
- Insomnia
Symptoms of Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Puffy face
- Skin dryness
- Cold sensitivity
- Muscle cramps
- Constipation
How is postpartum thyroid diagnosed?
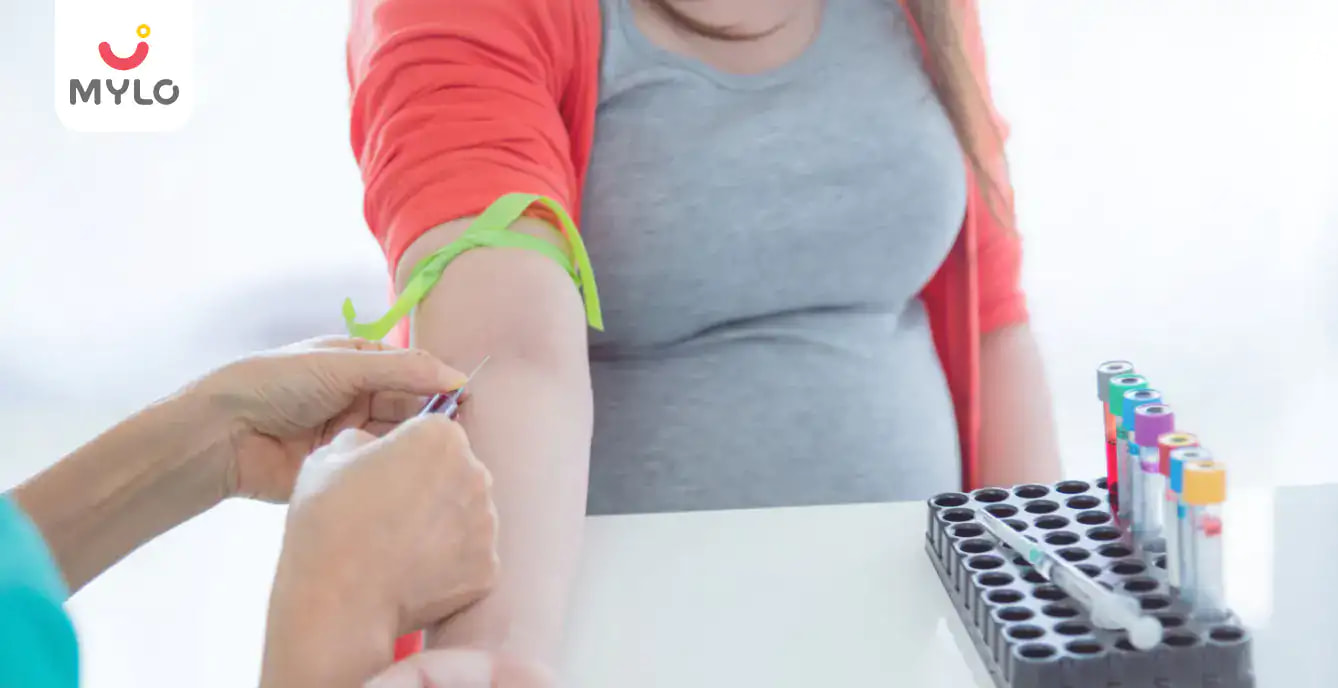
Postpartum thyroiditis is usually diagnosed using a Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) test and ultrasound. Women who have symptoms of postpartum thyroiditis should have their TSH level checked after giving birth.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is tested and considered normal if it is between 0.5 and 5.0 mU/L. If it is higher than that, it may indicate that postpartum thyroiditis could present a problem.
Ultrasound is used for diagnosing postpartum thyroiditis and is normally done three months after childbirth when the disease is likely to develop. The ultrasound may check for the presence of nodules and the size of the thyroid gland.
How is postpartum thyroiditis treated?
Postpartum thyroiditis is treated differently from Hashimoto's thyroiditis and other forms of autoimmune thyroiditis in that it does not require lifelong treatment. Most women with postpartum thyroiditis will get better without treatment within a year of delivery.
Postpartum thyroiditis treatment depends on the stage of the disease. In the early stages of postpartum thyroiditis, the patient can be treated with anabolic steroids, thyroxine, and beta blockers.
In the advanced stages, the patient is treated with steroid tablets and thyroid hormone treatment. Anti-thyroid medications may be given to a patient to treat hyperthyroidism during postpartum thyroiditis.
The prognosis is typically good, and most women with postpartum thyroiditis will eventually have a normal thyroid and return to a normal life.



Written by
Sanju Rathi
Get baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Questions
Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Hai.... My last period was in feb 24. I tested in 40 th day morning 3:30 .. That is faint line .. I conculed mylo thz app also.... And I asked tha dr wait for 3 to 5 days ... Im also waiting ... Then I test today 4:15 test is sooooo faint ... And I feel in ma body no pregnancy symptoms. What can I do .

Baby kicks KB Marta hai Plz tell mi

PCOD kya hota hai

How to detect pcos

Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |








