Home

Women Specific Issues

Pelvic Pain: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options
In this Article

Women Specific Issues
Pelvic Pain: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options
Updated on 8 January 2024
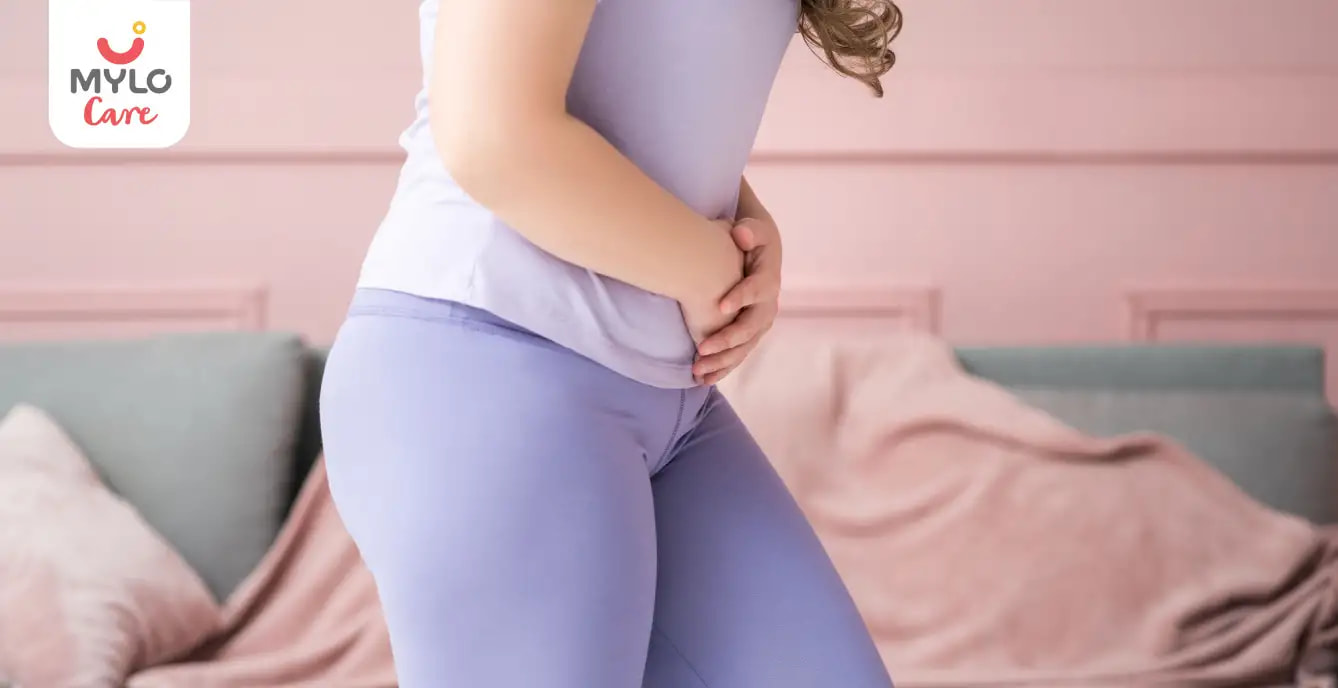
From a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations, pelvic pain can manifest in various forms. While some women may refer to it as ovary pain, others think of it as one sided pelvic pain. No matter the name, it can cause immense discomfort, disrupt daily activities, and significantly impact one's quality of life. In this article, we will understand its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
Where is pelvic pain located?
Pelvic pain is a common condition experienced by many individuals, particularly women. It refers to any discomfort or pain felt in the lower abdomen, between the hip bones. The pelvis is the area between the abdomen and the thighs, where various reproductive and urinary organs are located. Therefore, it can originate from a variety of sources, including the reproductive organs, bladder, or even the digestive system.
What does one sided pelvic pain feel like?
One-sided pelvic pain can be a cause for concern and may indicate a specific underlying condition. The type and intensity of pain can vary depending on the cause. For example, if the pain is originating from the left ovary, it may feel like a dull ache or a sharp, stabbing pain on the left side of the lower abdomen. It may also radiate down the leg or into the lower back. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause of the pain and receive appropriate treatment.
What are the reasons for pelvic pain?
Pelvic or ovary pain can have various causes, and it is crucial to identify the underlying reason for accurate treatment. Here are six common reasons:
1. Endometriosis
This is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and inflammation.
2. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
An infection of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by sexually transmitted infections, can lead to pelvic pain.
3. Ovarian cysts
Fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries can cause pain, particularly if they rupture or become twisted.
4. Uterine fibroids
Noncancerous growths in the uterus can result in pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, and other symptoms.
5. Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Infections in the urinary system, including the bladder and urethra, can cause pelvic pain.
6. Gastrointestinal issues
Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can also manifest as pelvic pain.
What are some other conditions that can lead to ovary pain?
Pain in the ovaries can be attributed to various conditions. Here are four additional conditions that can cause ovary pain:
1. Ovarian cyst torsion
When an ovarian cyst becomes twisted, it can lead to severe pain in the ovary.
2. Ovarian cancer
In rare cases, ovarian cancer may cause pain in the ovaries. It is important to seek medical attention if the pain persists or worsens.
3. Ovulation
Some women may experience mild right side ovary pain or left ovary pain during ovulation, known as mittelschmerz. This pain is usually short-lived and not a cause for concern.
4. Ectopic pregnancy
In cases where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, such as in the fallopian tubes, it can cause severe ovary pain and is considered a medical emergency.
Treatment options for pelvic pain
The treatment depends on the underlying cause and may vary from person to person. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Pain medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate mild to moderate pelvic pain.
2. Hormonal therapy
For conditions like endometriosis or uterine fibroids, hormonal treatments may be prescribed to regulate hormone levels and reduce pain.
3. Antibiotics
If pelvic pain is caused by an infection, such as pelvic inflammatory disease or a urinary tract infection, antibiotics may be necessary to eliminate the infection.
4. Surgery
In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove cysts, fibroids, or address other underlying conditions causing pelvic pain.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
FAQ’s
1. Why do I have pain in my left ovary?
Experiencing left ovary pain can be concerning. Several factors can contribute to pain in the left ovary, including ovulation, infection, ovarian cyst, endometriosis, etc. Seeking medical attention is essential to determine the exact cause of the pain and receive appropriate treatment.
2. Is it normal to experience right side ovary pain?
Experiencing pain on the right side of the lower abdomen, specifically in the ovary, can be a cause for concern. While some mild discomfort during ovulation can be considered normal, persistent or severe pain should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
3. How long does one-sided pelvic pain last?
The duration of one-sided pelvic pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some individuals may experience short-lived pain during ovulation, lasting only a few hours or days. In other cases, such as with conditions like endometriosis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome, the pain may be recurrent and last for extended periods, ranging from weeks to months. It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause of the pain and develop an appropriate management plan.
Key Takeaways
Pelvic pain can originate from various sources, including the reproductive organs, bladder, or gastrointestinal system. Understanding the location and characteristics of the pain can provide valuable insights into the underlying cause. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Treatment options may include pain medication, hormonal therapy, antibiotics, or surgical intervention depending on the specific condition causing the pain.
References
1. Long WN. Pelvic Pain. (1990). In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths
2. Dydyk AM, Gupta N. Chronic Pelvic Pain. (2023). [Updated 2023 Apr 1]. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.



Written by
Anandita Sharma
Drawing on more than a decade of expertise in administration, Anandita Sharma currently serves as a content operations e
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
What Power Pumping Schedule Works Best To Increase Breast Milk Supply?
Which Diaper Ingredients Should You Avoid For Sensitive Skin Babies?
Which Organic Disposable Diapers Are Safest for Newborns with Sensitive Skin in India?
How to Understand Diaper Price Range in India and Compare Cost per Diaper Before You Buy Online
Related Questions
Hello frnds..still no pain...doctor said head fix nhi hua hai..bt vagina me pain hai aur back pain bhi... anyone having same issues??

Kon kon c chije aisi hai jo pregnancy mei gas acidity jalan karti hain... Koi btayega plz bcz mujhe aksar khane ke baad hi samagh aata hai ki is chij se gas acidity jalan ho gyi hai. Please share your knowledge

I am 13 week pregnancy. Anyone having Storione-xt tablet. It better to have morning or night ???

Hlo to be moms....i hv a query...in my 9.5 wk i feel body joint pain like in ankle, knee, wrist, shoulder, toes....pain intensity is high...i cnt sleep....what should i do pls help....cn i cosult my doc.

Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Vaginal Discharge
Brown Discharge: Causes, Symptoms and When to Seek Help

Care for Baby
Baby Hair Style: A Complete Guide for Trendy Parents
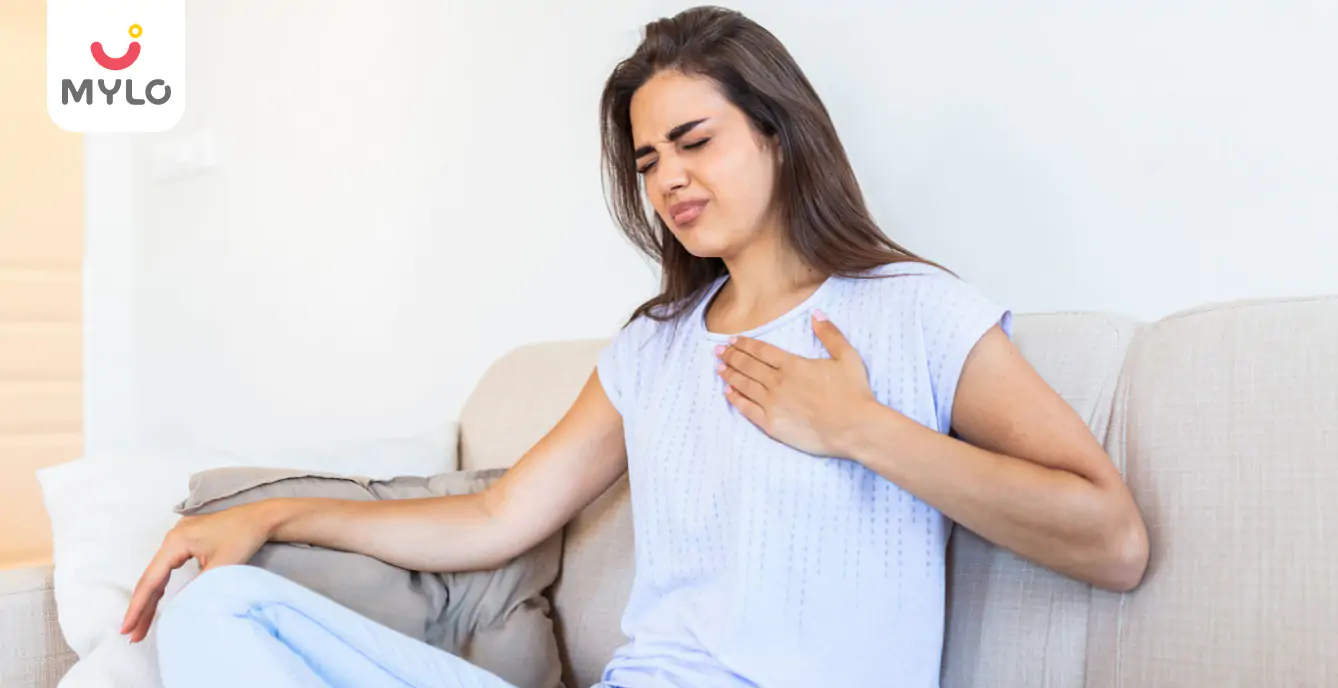

Ovulation
Breast Pain During Ovulation: A Comprehensive Guide on Causes and Solutions
Scans & Tests
PCOS Ultrasound: What to Expect During the Procedure
Women Specific Issues
Uterus Didelphys: Understanding Symptoms, Risks and Treatment Options
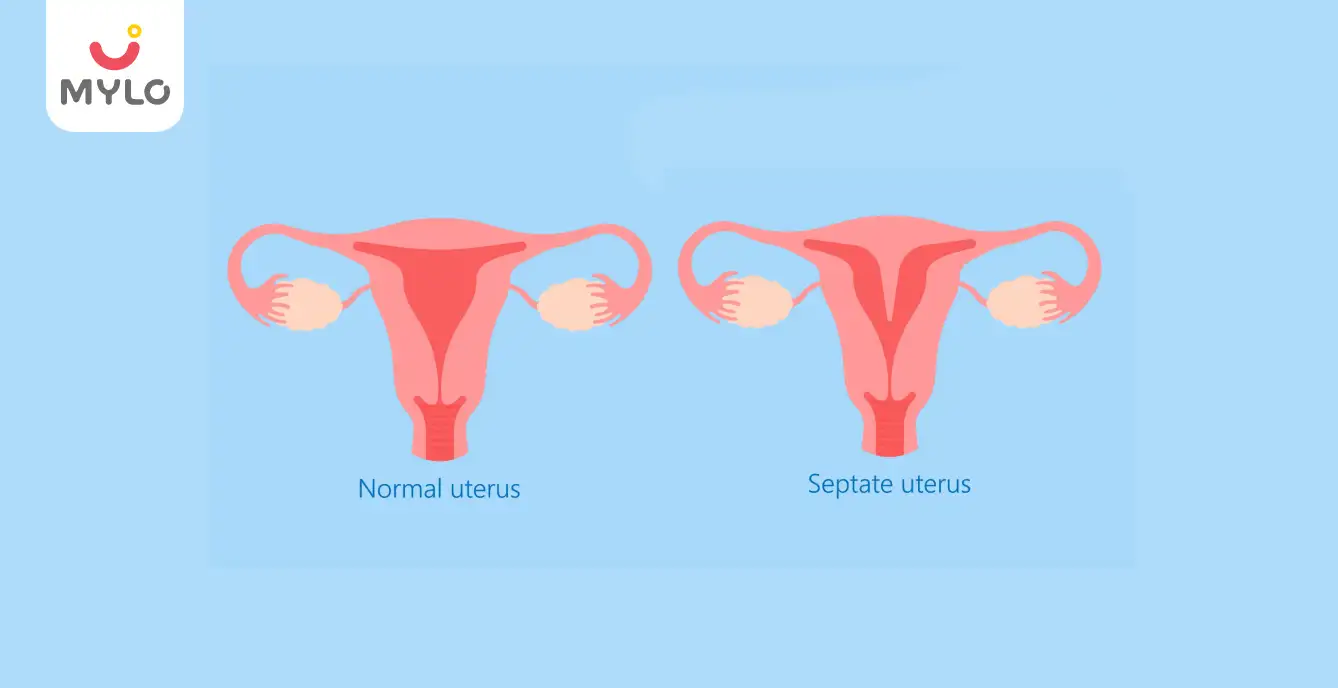
Women Specific Issues
Septate Uterus: A Comprehensive Guide on Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Options
- Should Pregnant Women Get Flu Shots
- Why you should choose a Vaginal Delivery? Know the pros & cons
- The Art of Painting When Pregnant: Tips for a Safe and Creative Experience
- Do Pregnant Women Get Their Period?
- A Guide to Precautions After Ovulation When Trying to Conceive
- Tight Vagina and Women's Health: An In-Depth Guide
- The Ultimate Guide to Using Olive Oil for Baby Massage
- Heat Rash During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms and Prevention
- The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Reasons for Late Period
- What Can Be the Maximum Delay in Periods If Not Pregnant?
- Black Period Blood: Is It Normal or a Cause for Concern?
- Lean PCOS: A Comprehensive Guide on Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- PCOS Mood Swings: The Ultimate Guide to Causes and Strategies for Relief
- PCOS and Thyroid: Understanding the Complex Relationship and Finding Solutions


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |




