Get MYLO APP
Install Mylo app Now and unlock new features
💰 Extra 20% OFF on 1st purchase
🥗 Get Diet Chart for your little one
📈 Track your baby’s growth
👩⚕️ Get daily tips

OR


Article Continues below advertisement
- Home

- Women Specific Issues

- Cervical Cancer: Causes, Symptoms & Prevention
In this Article
- What are the causes of cervical cancer?
- 1. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- 2. Sexual activity
- 3. Smoking
- 4. Compromised Immune system
- 5. History of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
- How is cervical cancer diagnosed?
- What is the treatment for cervical cancer?
- 1. Surgery
- 2. Radiation
- 3. Chemotherapy
- How to reduce your risk for cervical cancer?
- 1. Get vaccinated against HPV
- 2. Practice safe sex
- 3. Don't smoke
- 4. Check your risk factor
Women Specific Issues
 26735
26735Cervical Cancer: Causes, Symptoms & Prevention
Updated on 2 February 2024
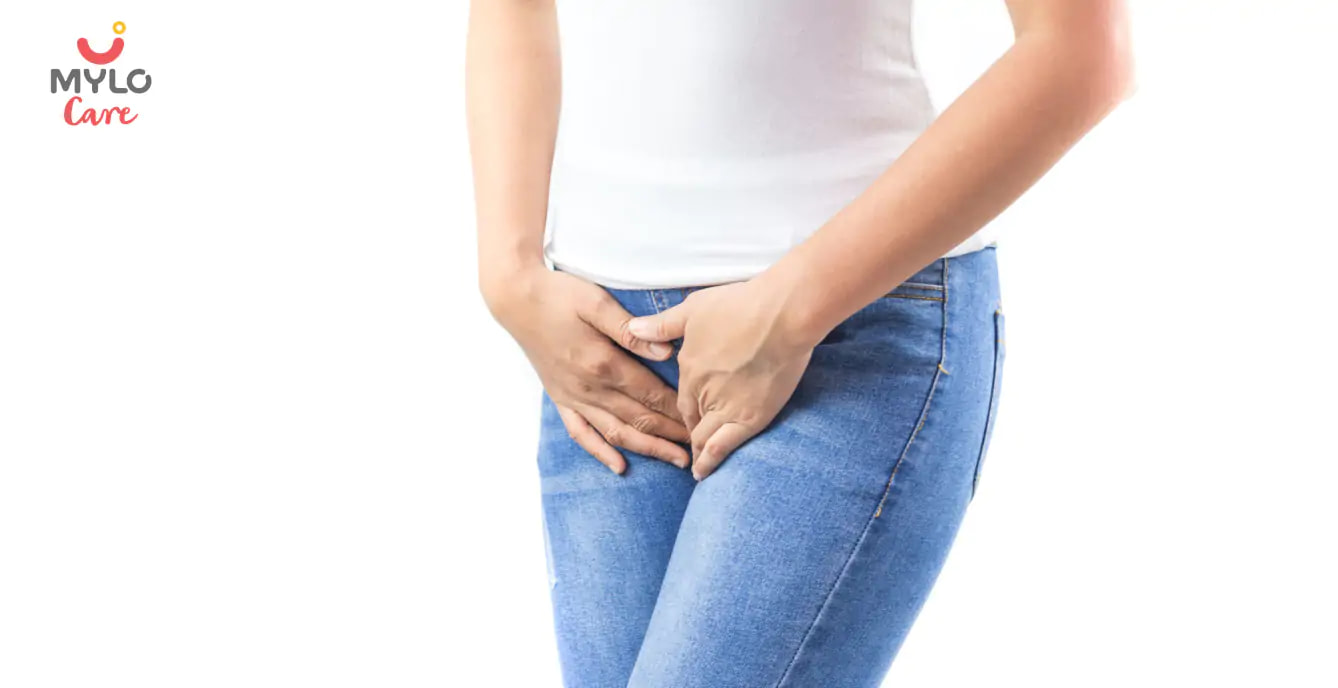
Cancer is defined as the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. There are over 200 types of cancers in the body, each of them named after the part of the body where it started. Cancer that starts in the cells of the cervix — the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina- is called cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer is the 4th most common cancer among women worldwide. Though women across all age groups are at risk of cervical cancer, mostly it occurs in women over the age of 30. In this article, we will understand the symptoms of cervical cancer, its causes, diagnosis and tests, treatment and prevention.
What are the causes of cervical cancer?
It isn't clear what causes cervical cancer but there are certain factors that increase a person's risk of developing cervical cancer such as:
Article continues below advertisment
1. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a group of viruses that are extremely common worldwide and are one of the most prominent causes of cancer. Two types of HPV (Type 16 & 18) cause 70% of cervical cancers. HPV is transmitted during sexual activity.
2. Sexual activity
Sexual activity has the potential to expose you to HPV. Women who become sexually active at a young age have an increased risk as the cervix changes during puberty and these changes make the cervix more vulnerable to damage. Women who have multiple partners also are at an increased risk. Besides intercourse, genital-to-genital skin contact and oral sex also constitute sexual activity.
3. Smoking
Smoking decreases the chance of an HPV infection going away on its own. A prolonged HPV infection increases your risk of developing cervical cancer.
4. Compromised Immune system
Factors like Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which causes AIDS, cripple the immune system and puts people at higher risk for HPV infections. The immune system is critical in destroying cancer cells and slowing down their growth.
5. History of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Certain bacteria like Chlamydia trachomatis, spread by sexual contact, can infect the genital tract of women. HPV and chlamydia together lead to a higher risk of cervical cancer.
Article continues below advertisment
What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer in its early stages usually doesn't produce any symptoms. However, a more advanced cervical cancer can produce the following symptoms:
- Vaginal bleeding between periods, after menopause and after sexual intercourse
- Bloody vaginal discharge of a watery consistency and a foul smell
- Pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse
How is cervical cancer diagnosed?
There are certain screening tests that can help identify cervical cancer and precancerous cells that may develop into cervical cancer. Screening tests such as Pap test and HPV DNA test are available for women over the age of 21.
If the doctor suspects cervical cancer, they will perform a biopsy (take a sample of cervical cells) for laboratory testing. If the doctor determines that you have cervical cancer, they may perform further tests such as X-ray, MRI, CT scan and PET and recommend the needed treatment.
What is the treatment for cervical cancer?
The treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage of cancer, any preexisting health conditions you may have and your preferences. Cervical cancer can be treated by surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or a combination of the three.
1. Surgery
Cervical cancer in the early stage is usually treated with surgery. However, it may or may not be the best treatment for you depending on the size of cancer, its stage and whether you want to become pregnant in the future.
Article continues below advertisment
2. Radiation
Using high-powered energy beams, radiation therapy helps to kill cancer cells. It can be used in combination with chemotherapy or after surgery if there’s a chance the cancer will come back. Radiation therapy can however cause menopause and problems in conceiving.
3. Chemotherapy
Using chemicals to kill cancer cells, chemotherapy is a drug treatment that can be given intravenously or through a pill. Chemotherapy can help treat advanced stages of cervical cancer.
How to reduce your risk for cervical cancer?
There are some preventative measures you can take to reduce your risk of cervical cancer such as:
1. Get vaccinated against HPV
As most cervical cancers are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). Widespread vaccination for HPV will reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer. Contact your doctor to find the right vaccine for you.
2. Practice safe sex
The best way to prevent cervical cancer is to avoid any sexual contact with people infected with HPV, use protection and insist that your sexual partner goes through an STD panel test before you get intimate.
Article continues below advertisment
3. Don't smoke
Not only smoking destroys your lungs, but it also prevents your body from fighting infections like HPV.
4. Check your risk factor
Some women are at a higher risk factor for cervical cancer than others. Talk to your doctor about this and find out if you're at risk.



Written by
Priyanka Verma
Priyanka is an experienced editor & content writer with great attention to detail. Mother to an 11-year-old, she's a ski
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Education
The A-Z Guide to Identifying Stem Vegetables for Kids
(2,033 Views)

Fetal Heartbeat
Can Fetal Heartbeat Disappear and Reappear?
(35,860 Views)

Education
The Ultimate Guide to Teaching Children 20 to 30 Tables
(1,651 Views)

Education
GK Questions for Kids from Nursery to Class 6
(3,847 Views)

Growth & Development
Height and Weight Chart for Boys and Girls in India
(38,981 Views)

Education
The A-Z Guide to Identifying Winter Vegetables for Kids
(1,775 Views)
- Dalia in Pregnancy: A Superfood for the Health of Both Mom and Baby
- 1st Birthday Wishes for Your Little One's Big Day
- The Ultimate Guide to Consuming Litchi During Pregnancy
- Almonds in Pregnancy: Cracking the Nutty Secret to Their Benefits
- Popping the Question: Is It Safe to Indulge in Popcorn in Pregnancy?
- Cherry Fruit in Pregnancy: What Every Expectant Mother Should Know
- The Ultimate Guide to Consuming Pista During Pregnancy
- Sugarcane Juice in Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions
- The Ultimate Guide to Consuming Mushroom in Pregnancy
- The Ultimate Compilation of GK Questions and Their Answers
- The Ultimate Compilation of 2 Letter Words for Children
- The A-Z Guide to Identifying Root Vegetables Names for Kids
- 11 to 20 Table: A Complete Overview for Children
- Tables 1 to 10: A Complete Overview for Children


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION
Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award
Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN
















At Mylo, we help young parents raise happy and healthy families with our innovative new-age solutions:
- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |